5HRF Managing and Coordinating the Human Resource Function
- June 25, 2021
- Posted by: admin
- Category: CIPD Level 5

The purpose of managing and coordinating HR function is to expose the learner to the duties and activities performed in HR. In addition, this course assists the student in comprehending the HR function’s position in the company.
This course assists students in focusing on the HR professionals’ objectives that they should establish in the HR department to fulfil the organisation’s aims.
The objective of the managing and coordinating HR function is to familiarise the learner with the tasks and responsibilities of HR. Furthermore, this course aids the student in grasping the HR function’s role in the organisation.
This course helps students focus on the Human resource objectives they should create in the HR department to meet the organisational goals. HR functions vary as the organisation evolves, so this unit will expose learners to HR’s duties to ensure success in a changing business.
Learners should comprehend the many theories covered in this unit to guarantee that HR services are given to the business to succeed effectively.
Objectives delivered by the HR function
Within an organisational framework, human resource professionals perform a variety of duties. This task entails the following:
1. Staffing is the process of identifying and performing recruiting to satisfy the needs of the organisation’s HR responsibilities. This approach employs various scientific ways to gather many applicants and screen them for high-level abilities.
Following the recruitment of skilled and experienced individuals, the HR function’s next duty is to offer resources to support the organisation’s continuous growth. HR is responsible for overseeing ongoing growth and does so by:
- Preparing reports for organisation leaders and conveying feedback to employees.
- Educating new employees about their duties and responsibilities in the organisation.
- Organising training seminars to ensure that employees are more equipped in their particular professions. (HR coordinates day to day task).
2. Salary and Benefits: HR departments are responsible for determining suitable remuneration based on various duties, performance, and legal requirements. Other activities that are under-compensated include:
- Setting market-based compensation levels by using benchmarks such as industry norms for a specific job description.
- Agreeing on health insurance prices, retirement plans, and other benefits with third-party providers.
- Talking to employees about a pay raise or a pay cut.
- Ensuring that employees follow all legal and cultural requirements.
3. Employee and Labor Relations: HR’s responsibility is to protect employees’ rights by collaborating with unions and settling conflicts between the business and its HR. This activity entails:
- Arbitrating disagreements between employers and workers
- HR can resolve a conflict amongst employees.
- HR may negotiate with unions, top-level management, and other stakeholders on behalf of employees.
- When it comes to any more significant organisational problem involving employee welfare, HR serves as the organisation’s and employees’ voices.
• Investigate and resolve allegations of harassment and other forms of abuse.
4. Health & Safety: Employees’ safety and health must come first in every industry to succeed. The following activities are part of this activity:
- HR functions ensure that legal requirements are adhered to in any job description for safety measures.
- HRM practices ensure that legal requirements for safety measures are adhered to in any job description for safety measures.
- Safety compliance is presented to the necessary legal agencies.
- Meeting with unions to discuss safety and compliance.
This course requires students to understand HR functions and link them to those necessary in any industry’s human resource profession. In the picture below, these functions have been simplified.
Delivery of HR objectives to the organisation
The primary goal of companies is to guarantee that the organisation’s goals are met. For this to work, management must guarantee that employees are given clear instructions on what they should do. This communication takes place from the bottom up, from employees to the highest levels of management.
This course requires students to comprehend senior management’s involvement in the organisation’s operations and how senior management contributes to the performance of HR activities.
Learners must comprehend that HR is in charge of extensive information about the company and that the senior management is in charge of essential duties beyond the scope of human resource capabilities. As a result, a senior manager is required to assist human resource departments in ensuring that their assigned duties are completed.
These top executives also make sure that HR functions are following the organisation’s mission and goals. Other employees in the company strive to achieve the organisation’s goals and objectives and the senior manager’s responsibilities.
The learners will benefit from this unit because they will get a better understanding of the roles and duties of various stakeholders in enhancing the value of the company and guaranteeing the attainment of its goals.
Change management theories
Organisations are continuously changing, and HR departments must assess how this change affects the organisation’s goals. To do so, the student must first comprehend the theories that are utilised to assess these changes.
These are the theories:
The McKinsey 7-S Framework: Although this model appears to be complicated, it is essential for determining the extent to which changes affect the company. This model consists of seven models that are evaluated in the order in which they impact one another. This component is:
- Staff: This aspect addresses each employee’s capacity in the organisation
- Skills: This element reflects each employee’s competency in the organisation
- Systems: This component outlines the task and method that employees must follow to perform their job.
- Strategy: The organisation’s plan to improve its competitive edge is described in this part.
- Structure: The organisation’s hierarchy is described by this element.
- Shared Values: These are the organisational culture’s and general work ethics’ fundamental values.
The change model of Kurt Lewin is as follows: As seen in the diagrams below, this theory is explained in three phases.
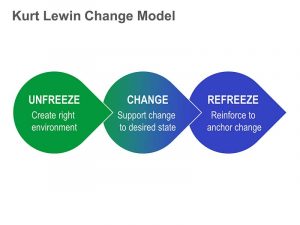
- Unfreeze: In this step, you must “unfreeze” or halt the present process and assess what may be improved.
- Change: This phase executes the necessary changes once HR has educated everyone on why change is essential.
- Freeze: During this phase, the organisation aims to either be solidified or put to work on the recently adopted change.
Nudge Idea: This theory proposes a change and backs it up with facts to persuade employees to make the change.
Kübler-Ross Change Curve, ADKAR Change Management Model, and Bridges’ Transition Model are other change theories. This model will provide students with the information essential to assist in analysing and implementing essential changes in any company.
Learning outcomes
By the completion of this unit, students should:
- Recognise the HR function’s purpose as well as essential duty in an organisation
- Comprehend how HR objectives are deployed at various levels in an organisation.
- Comprehend how HR functions are valued and how the organisation is functioning
- Recognise how HR interacts with other departments inside the company.
Conclusion
This class is designed for students who want to improve their professionalism and career possibilities in HR management. This course teaches the student what abilities are required for HR duties, how to execute change, settle employee dispute, and monitor the success of organisational objectives.
Finally, HR professionals involved in executing organisational plans and policies should take this unit to guarantee that the organisation’s procedures are carried out smoothly.


